Comparing defi to traditional lending/borrowing
The growth of defi has challenged the traditional financial industry, prompting a comparison between the two. This write-up explores how defi lending/borrowing differs from traditional finance. You’ll also discover what common points both lending types have, what advantages they offer, and what limitations both systems impose when accessing capital.
Lending & Borrowing as Building Blocks
Lending and borrowing are two related concepts in finance. Let’s define each term to better understand how the finance system functions.
- Lending refers to providing money or other resources to other market participants (borrowers) with the expectation that the loan will be repaid with interest.
- Borrowing refers to the act of obtaining money or other resources from other market participants (lenders) with the understanding that it will be repaid with interest. Borrowing allows individuals and businesses to access funds they may not have, enabling them to make investments, purchase goods and services, and grow their operations.
Lending and borrowing provide essential liquidity to the economy, thus stimulating the flow of money and resources within the system. The interaction of lenders and borrowers eventually creates a credit and debt cycle that helps drive economic growth and prosperity.
How Lending Works
Lending involves two parties: a borrower and a lender. The lender will usually require the borrower to provide collateral as security against the loan in case the borrower defaults on their payments. The loan will then be repaid over a period of time, typically with interest payments. The interest rate can vary depending on the lender, the terms of the loan, and the borrower’s credit score.
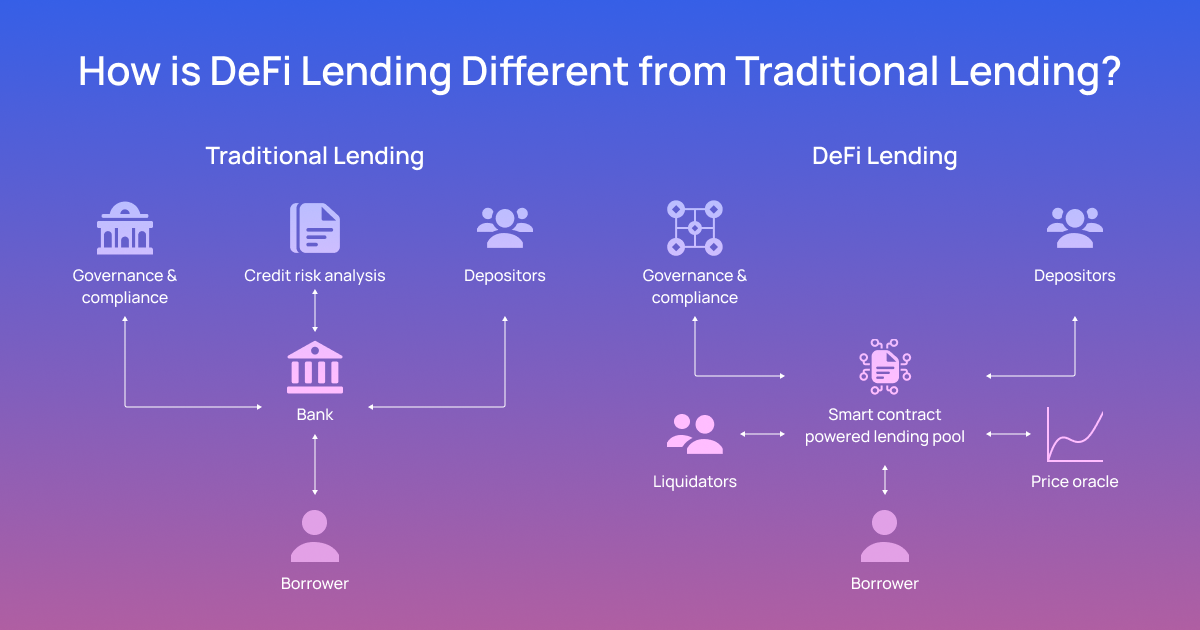
Traditional Lending
Traditional lending typically involves a financial institution, such as a bank or credit union, providing a loan to an individual or business. The borrower typically goes through an application process that includes submitting personal and financial information, such as income, credit history, and assets. The lender evaluates this information to determine the borrower’s creditworthiness and the terms of the loan, including the interest rate, repayment period, and collateral requirements.
Traditional lending heavily relies on three pillars to assess the person’s financial health or creditworthiness.
- Credit score
- Collateral
- Reputation
The Credit Score
The credit score is used to assess how likely a person is to repay a loan or other form of debt. It comprises the following.
- Payment history
- Amounts owed
- Length of credit history
- Types of credit used
- New credit
Collateral
Collateral is an asset or property that a borrower pledges as security for a loan. In the event that the borrower is unable to repay the loan, the lender can seize the collateral to recover the outstanding debt. Collateral serves as a form of security for lenders, reducing their risk and increasing their trust in the borrower’s ability to repay.
Reputation
Borrowers who have a good reputation in their community or industry are more likely to be trusted by lenders. Reputation can be built through consistent and responsible financial behavior, ethical business practices, and a track record of successful ventures. In some sense, reputation is the credit score over time.
Decentralized Lending
Most defi lending protocols have two things in common:
- Use collateral evaluation instead of the traditional centralized credit assessment. defi lending uses collateral as the repayment guarantee vehicle.
- Use smart contracts to manage crypto-assets. A smart contract is a program that runs on a distributed ledger (like the Ethereum blockchain). It can do bookkeeping and calculations, receive and hold digital assets, and execute transactions automatically when certain events occur.
These protocols enable users to lend/borrow without third parties like banks. Instead, users can borrow funds from a pool of lenders, who can provide the funds at a predetermined rate of interest. The loan agreement is enforced in a decentralized manner, using smart contracts, and the repayment of the loan is typically done through digital assets.
The Current State of Lending & Borrowing
AI technologies and new lending models have already disrupted traditional lending/borrowing markets, making financial services more accessible to a broader range of people.
One example is online platforms like FinTech Zest Finance using algorithms and data analysis to evaluate creditworthiness, reducing the time and cost of underwriting loans. This has created new opportunities for borrowers, particularly those who may have difficulty accessing credit through traditional channels.
On a lighter note, there may still be room for innovative lending models to make the financial system more adaptable and resilient in the face of change.
Traditional Lending
Lending is one of the most important pillars of the financial system. According to a report by the Institute of International Finance, the global issuance of sustainable debt reached $306 trillion back due to a strong US dollar and high-interest rates in 2022.
The finance markets assume various forms of lending, like consumer lending, student loans, mortgages, corporate debt, government bonds, and more. However, traditional lending methods share three core drawbacks: (merged for simplicity)
- A lack of transparency
- Difficulty in accessing capital
- Slow decision-making
In this section, we’ll briefly cover these generalized issues. To learn more about specific issues, check out the next section on how defi lending disrupts the finance markets.
Poor Transparency
Borrowers may not fully understand the terms and conditions of the loan. Additionally, lenders may not have full visibility into the financial situation of the borrower, which can increase the risk of default. This lack of transparency can lead to a breakdown in trust and may ultimately result in negative outcomes for both parties.
Challenging Access to Capital
Banks and other traditional lending institutions have strict lending criteria, which often exclude individuals or small businesses. The lengthy application and approval process can also delay access to much-needed capital.
Slow Decisions
Traditional lending is cumbersome because multiple parties are involved. Any intermediaries like underwriters, loan officers, and others who supervise the application eventually slow the lending process down. Additionally, there may be a lot of paperwork and documentation required, which can further the delay.
Slow decision-making expands beyond the lending itself, reflecting the industry psychology per se rather than the mere lending cycle.
Although traditional lending has historically lacked innovations — due to lenders unwilling to take risks and try out new lending models — the products offered were put together pretty well and only required slight edits over the years. The rationale behind the minimal change is best explained by convenience for the end users, their habits, and the lack of alternatives.
Raymond Loewy, a renowned French industrial designer, believed that when it comes to consumer habits, people are caught in the middle of two conflicting forces: neophilia, the attraction to new things, and neophobia, the fear of the unfamiliar. He coined the term MAYA, or “Most Advanced Yet Acceptable”, which basically proposed finance must be familiar enough for consumers to understand it, yet also contain enough of a twist.
Defi is one of the ways to do so, as it catches a striking balance between familiarity and novelty and further turns relevant in the face of traditional economic challenges cascading upon us.
The Defi Lending Revolution
Any form of lending is intricately related to the concept of trust and the promise of repayment. The bond is so strong that the term “credit” itself dates back to the mid-16th century French, meaning to believe and trust. Let’s now focus on why decentralization could be an efficient way to tackle the inefficiencies of traditional finance.
A decentralized finance system directly addresses the challenges of traditional lending because it’s built on blockchain technology. Blockchain solves the following issues.
Passthrough issues
Information asymmetry between borrowers and lenders and inefficient data flow, leading to delays and higher costs. Blockchain technology solves these issues by creating a more efficient and transparent data flow.
Intermediary cost
Intermediary costs are fees charged by middlemen, like banks, to facilitate financial transactions. Defi’s smart contracts eliminate these costs, providing better transaction rates, security, transparency, and lower costs.
Lack of trust
Borrowers are concerned about transparency, fairness, and security of their personal and financial information. Lenders worry about the borrower’s creditworthiness, the risk of default and recovering funds. Defi solves the trust issue through blockchain’s immutable and transparent technology.
Financial inclusion
Many people are edged from the traditional lending system, limiting their opportunities to access capital and build financial stability. Defi provides easier access to capital due to the underlying logic of lending.
Liquidity inefficiency
Traditional lending mechanisms produce suboptimal liquidity outcomes because supply and demand are divided into siloed markets. This division can result in oversaturation in one market and an inability to move that surplus to meet demand in another. defi lending is more flexible in this regard.
Traditional vs defi Compared
Let’s consider interest rates and collateral when dealing with the lending/borrowing markets to understand how both traditional and Defi lending perform.
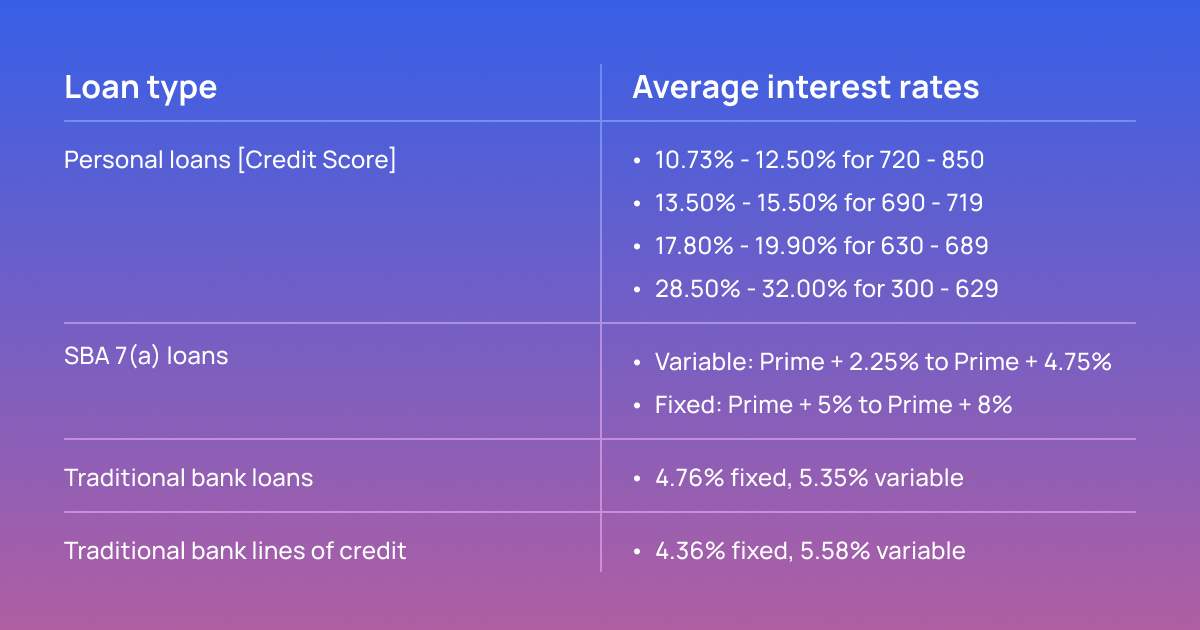
The Interest Rates Compared
The table below represents ballpark figures for interest rates one can find when dealing with the traditional lending framework. Note that all rates vary depending on loan amounts and terms.
Click here to check more numbers.
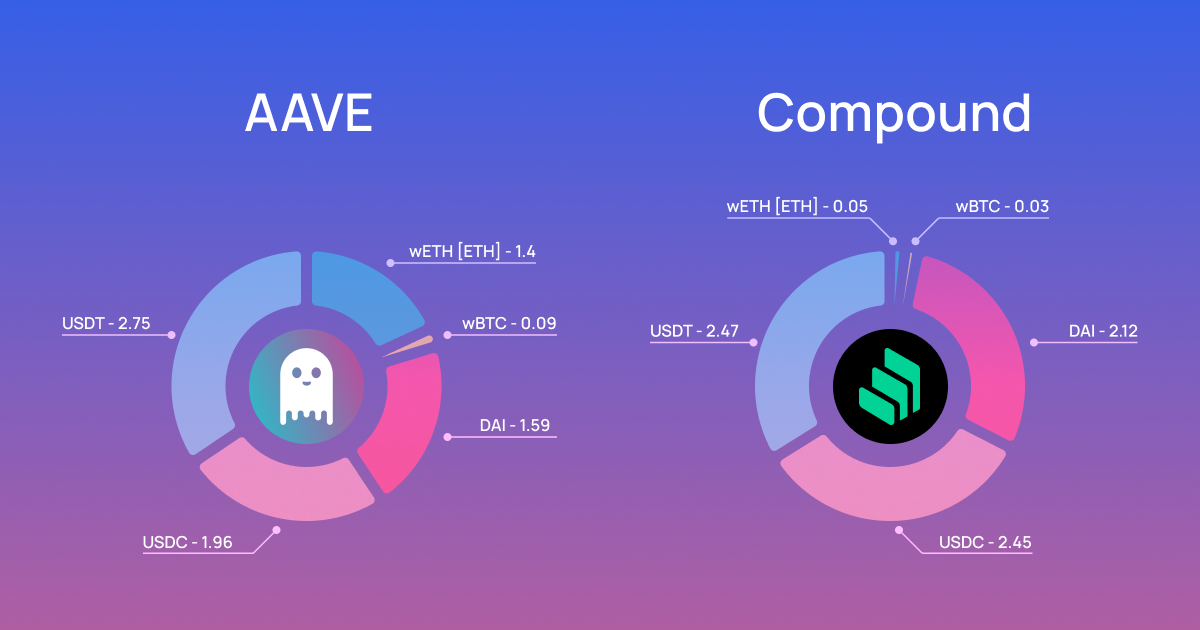
The State of Defi Interest Rates
The Collateral Rates Compared
Collateral requirements for traditional lending and decentralized lending can differ in several ways, including the types of collateral that are accepted, the level of over-collateralization required, and the process for determining the value of the collateral.
Traditional Collateral Requirements
In traditional lending, collateral requirements can vary depending on the type of loan, the borrower’s creditworthiness, and the lender’s risk tolerance. Collateral can include physical assets like real estate or vehicles, financial assets like stocks or bonds, or other forms of value like cash deposits.
The amount of collateral required is usually based on a loan-to-value (LTV) ratio, which is the ratio of the loan amount to the value of the collateral. LTV ratios can vary widely depending on the lender but typically range from around 70% to 90% (manually compared).
- Mortgages: Generally require a down payment of 3–20% of the home’s value, with the loan amount not exceeding 80–97% of the home’s value. The home serves as collateral for the loan.
- Car loans: Generally require a down payment of 10–20% of the car’s value, with the loan amount not exceeding the car’s value. The car serves as collateral for the loan.
- Personal loans: Generally do not require collateral but may have higher interest rates and stricter credit requirements.
- Secured personal loans: Require collateral such as a savings account, CD, or other assets. The loan amount is typically a percentage of the collateral’s value.
- Business loans: Collateral requirements can vary widely depending on the lender and the type of loan. Some lenders may require collateral in the form of business assets or a personal guarantee, while others may not require collateral at all.
Traditional lenders typically use appraisals or other valuation methods to determine the value of physical assets and may rely on credit scores or other indicators to assess the creditworthiness of borrowers.
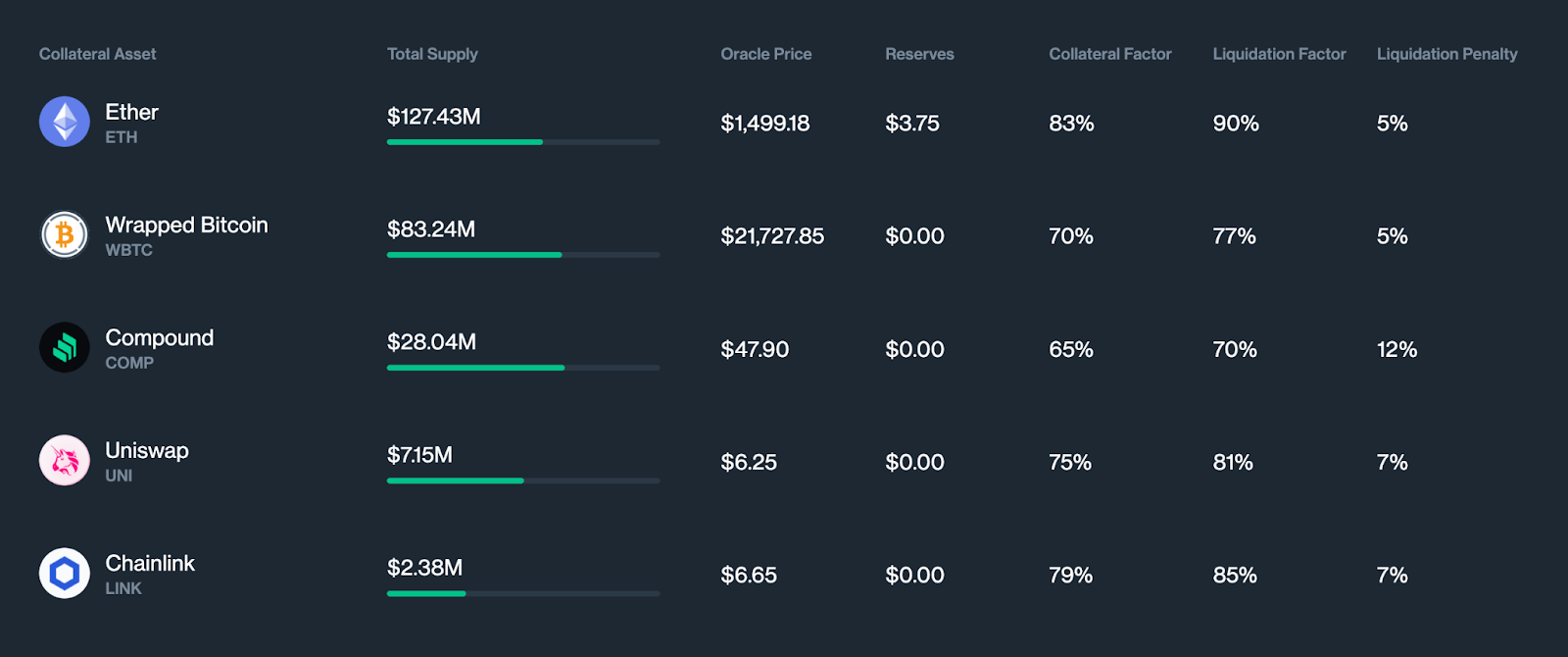
Defi Collateral Requirements
In decentralized lending protocols like Aave and Compound, collateral requirements are also based on an LTV ratio, but the types of collateral that are accepted are typically limited to tokenized digital assets.
The level of defi collateralization is often higher than in traditional lending, ranging from around 120 to 150% of the loan amount, and up 200% or more in some cases. This means that borrowers need to provide a significantly higher amount of collateral than the loan amount in order to secure a loan.
- On Aave, the collateral requirement is generally around 150% of the borrowed amount. That means you would need to put up at least $150 worth of collateral to borrow $100 worth of another asset.
- On Compound, the collateral factor for popular assets ranges from 65% to 83% as of writing. That means you can borrow up to 83% of the value of your deposit.
It’s important to note that the value of the collateral is determined by market prices for the digital assets being used as collateral, which can be subject to significant volatility and price fluctuations. In other words, these specific numbers can change over time as the protocols adjust their collateral requirements based on market conditions and other factors.
Traditional & defi Lending Risks
Let’s consider risks related to both traditional and decentralized lending.
Traditional Lending Risks
- Privacy & Reputation Risks. Participating parties can be identified. Lenders are subject to reputational risks. The lender’s reputation may be affected if the loan does not turn out as expected.
- Credit Risk. Credit risk involves the risk that a borrower may not be able to pay back the loan on time or at all
- Interest Rate Risk. Interest rate risk is the potential for loss due to changes in the interest rate.
- Liquidity Risk. Liquidity risk involves the risk that a lender may not be able to obtain funds quickly and easily when needed.
- Market Risk. Market risk is the risk that the value of the loan may decrease due to changing market conditions.
- Political Risk. Political risk is the risk that the government may interfere with the loan and make it difficult for the lender to collect what is owed. Moreover, loan contracts can be flexible, meaning that loan officers may modify terms to some extent
- Operational Risk. Operational risk involves the risk of loss due to operational errors or mistakes.
- Fraud Risk. Fraud risk is the risk that a borrower may attempt to defraud the lender by providing false information or taking the money and not paying it back.
- Exchange Rate Risk. Exchange rate risk is the risk that the value of the loan may decrease due to changes in the exchange rate.
Defi Lending Risks
Two core risks related to defi lending are collateral concerns and a price-liquidity feedback effect.
Collateral risks
Defi lending uses a non-recourse debt contract with over-collateralization as the sole risk control, which carries risks for both borrowers and lenders. The lender can only recoup the collateral’s value if there is liquidation, limiting the borrower’s liability. The over-collateralization requirement reduces the lender’s risk, but borrowers must pledge more collateral than the loan value. Also, there is an information asymmetry between borrowers and lenders regarding the collateral’s value. Defi lending can be less attractive than traditional options due to a bit limited capital access.
A Price-liquidity Feedback Effect
The Price-liquidity Feedback Effect is the relationship between asset prices and market liquidity. In defi lending, higher price expectations lead to more demand for lending, creating a self-fulfilling cycle that increases asset value and collateral. But, it can also create fragility in defi lending, causing sudden shifts in market sentiment and behavior, which creates fluctuations and risk that impact market stability.
Here’s the list of some other risks:
- Custody risks. A digital wallet helps protect access, but if the key is lost or stolen, the assets are most likely will be lost.
- Smart contract risks. defi is open source, which implies it’s more attackable than closed-loop systems. Smart contracts may have logic errors, which entail mispriced assets and flash loan attacks.
- Oracle risks. Smart contracts price assets based on external data feed. If the internal-external connection is broken, the contract might not work properly.
- Regulatory risk. The government may struggle to find the perfect regulatory balance. Too strict or soft regulations may significantly affect the market.
Wrapping Up
While traditional lending has been the cornerstone of the financial system for decades, decentralized lending through protocols like Aave and Compound has emerged as a viable alternative.
Decentralized lending offers significant advantages, including lower collateral requirements, faster decision-making, and lower interest rates. Additionally, the use of smart contracts eliminates intermediaries, which leads to lower transaction costs and improved transparency.
Although decentralized lending is still in its early stages and faces some challenges, the current trend suggests that decentralized lending has every chance to grow, and it may soon become a standard part of the lending landscape.